Master's thesis
This master’s thesis aims to find the best algorithm for semantic understanding of natural dialogs. The result can be used in a conversation AI. A part of the thesis is also a dataset, based on needs for a chatbot application for open-domain and which was based on real conversations. The thesis also identifies and examines sequential machine learning algorithms for intent and entity recognition. The result of the thesis is a detailed comparison of the selected algorithms regarding accuracy, memory requirements and computational complexity. Based on the results, a new model which joins intent and entity recognition together is created.
Keywords
- intent recognition
- entity recognition
- machine learning
- natural language processing
Results:
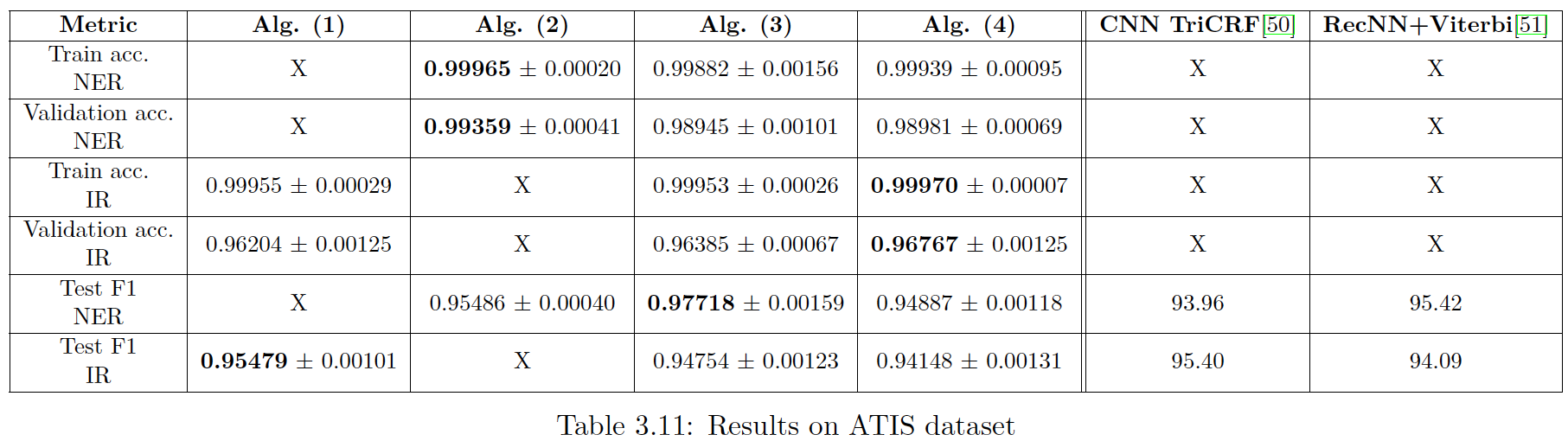
where
- (1) Measure best model for IR on generated data
- (2) Measure best model for entity recognition on generated data
- (3) Combine best model for entity recognition and IR
- (4) Combine Attention layer with RNN + ELMo - similar to [13]
The main result of the master’s thesis is proving that the joint models are, in general, preserving the NER accuracy and decreasing the intent recognition error rate. In our experiment we compare results of our joint model with published results in the scientific papers. The joint model is proven to be more efficient and requires less computational resources over separated models for each task.
Data
A PDF document of my master’s thesis.
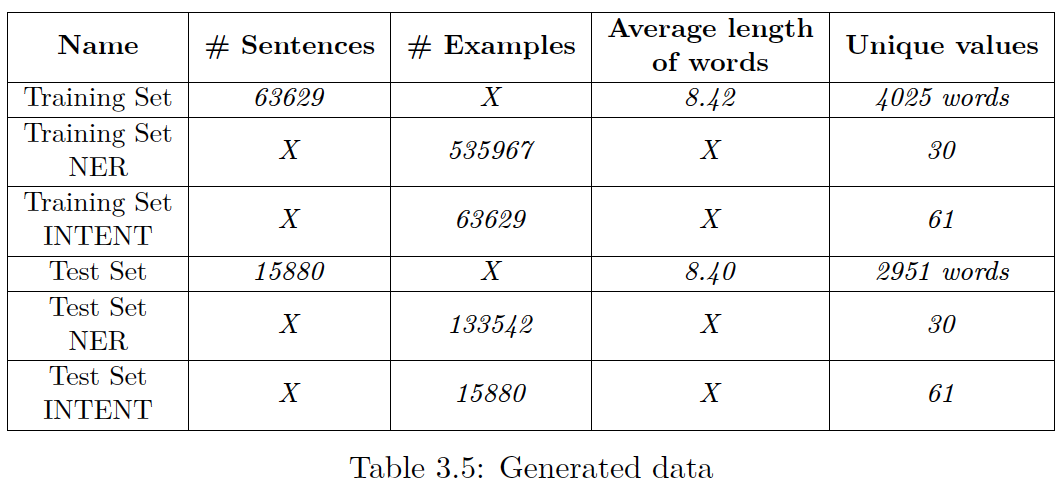
Generated data can be downloaded here.
References
- [13] Ma, M.; Zhao, K.; et al. Jointly Trained Sequential Labeling and Classification by Sparse Attention Neural Networks. CoRR, volume abs/1709.10191, 2017, [Online; accessed 25-December-2018], 1709.10191. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10191